Publications

People’s perception of forensic evidence is greatly influenced by crime TV series. The analysis of the human voice is no exception. However, unlike fingerprints—with which fiction and popular beliefs draw an incorrect parallel—the human voice varies according to many factors, can be altered deliberately, and its potential uniqueness has yet to be proven. Starting with a cursory examination of landmarks in forensic voice analysis that exemplify how the voiceprint fallacy came about and why people think they can recognize people’s voices, we then provide a thorough inspection of over 100 excerpts from TV series. Through this analysis, we seek to characterize the narrative and aesthetic processes that fashion our perception of scientific evidence when it comes to identifying somebody based on voice analysis. These processes converge to exaggerate the reliability of forensic voice analysis. We complement our examination with plausibility ratings of a subset of excerpts. We claim that these biased representations have led to a situation where, even today, one of the main challenges faced by forensic voice specialists is to convince trial jurors, judges, lawyers, and police officers that forensic voice comparison can by no means give the sort of straightforward answers that fingerprints or DNA permit.
Acquiring a consistent accent and targeting a native-standard-like Received Pronunciation (RP) or General American (GA) are prerequisites for French learners who plan to become English teachers in France. Reliable methods to assess learners’ productions are therefore extremely valuable. We recorded a little over 300 students from our English Studies department and performed auditory analysis to investigate their accents and determine how close to native models their productions were. Inter-rater comparisons were carried out; they revealed overall good agreement scores which, however, varied across phonetic cues. Then, automatic speech recognition (ASR) and automatic accent identification (AID) were applied to the data. We provide exploratory interpretations of the ASR outputs, and show to what extent they agree with and complement our auditory ratings. AID turns out to be very consistent with our perception, and both types of measurements show that two thirds of our students favour an American, and the remaining third, a British pronunciation, although most of them have mixed features from the two accents.
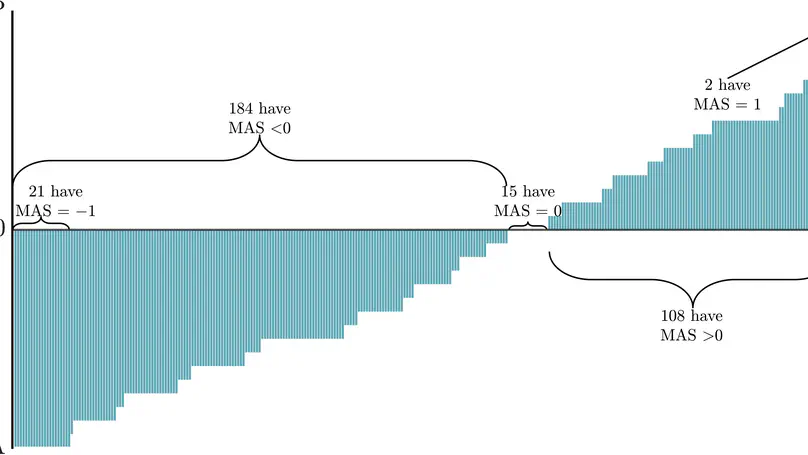
English and French have different phonological systems (Roach, 2009; Walker, 2001) and French learners have difficulties perceiving some contrasts, such as the approximants /w/ – /r/ (Hallé et al., 1999). They also tend to assimilate multiple English vowels to a single L1 category (Iverson & Evans, 2007). General American exhibits a raising of /æ/ in nasal environments (Carignan et al., 2016), thus creating an acoustic proximity between /æ/ and /ɛ/. The purpose of the present study was to assess the influence of CVN contexts on the perception of vowels by French university students. We addressed this issue as part of a pedagogical project called SEPALE, which consists of identification and discrimination exercises involving English phonemic contrasts and within which we explored the issue of nasalisation. Thirteen Californian speakers were recorded reading CVC and CVN words, to create stimuli used by undergraduate students in discrimination and perception tasks. Their answers were recorded in logfiles, used in our analysis. We found a higher proportion of errors when /æ/ – /ε/ and /ɑ/ – /ʌ/ were in a pre-nasal position and the first contrast yielded better identification and discrimination rates than /ɑ/ – /ʌ/. This finding could inform teachers’ choices of perception or production exercises.
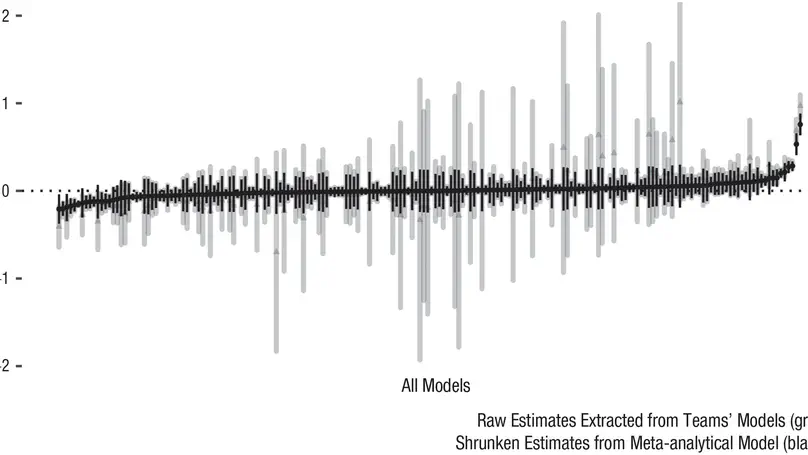
Recent empirical studies have highlighted the large degree of analytic flexibility in data analysis that can lead to substantially different conclusions based on the same data set. Thus, researchers have expressed their concerns that these researcher degrees of freedom might facilitate bias and can lead to claims that do not stand the test of time. Even greater flexibility is to be expected in fields in which the primary data lend themselves to a variety of possible operationalizations. The multidimensional, temporally extended nature of speech constitutes an ideal testing ground for assessing the variability in analytic approaches, which derives not only from aspects of statistical modeling but also from decisions regarding the quantification of the measured behavior. In this study, we gave the same speech-production data set to 46 teams of researchers and asked them to answer the same research question, resulting in substantial variability in reported effect sizes and their interpretation. Using Bayesian meta-analytic tools, we further found little to no evidence that the observed variability can be explained by analysts’ prior beliefs, expertise, or the perceived quality of their analyses. In light of this idiosyncratic variability, we recommend that researchers more transparently share details of their analysis, strengthen the link between theoretical construct and quantitative system, and calibrate their (un)certainty in their conclusions.
English /r/ takes different tongue shapes from one speaker to another. It is well-established that tip-down and tip-up shapes produce perceptually similar outputs. However, it remains unclear why speakers intuitively acquire one type or another. The present study considers the hypothesis that rhotic and non-rhotic varieties of English may influence the acquisition of different tongue shapes. We provide articulatory data on the pronunciation of English /r/ by 19 French learners of English, 10 with rhotic and 9 with non-rhotic accents. Ultrasound tongue images were recorded for onset and coda /r/ in various vocalic contexts and were classified as either tip-up or tip-down. Although rhoticity as a predictor of tongue shape does not reach statistical significance, we found a tendency for rhotic speakers to use a higher proportion of tip- down shapes. We conclude that while rhoticity may partly influence tongue shape, other factors are alsoat play, including co-articulatory constraints

Après avoir procédé à une analyse de la représentation de l’expertise vocale dans les séries policières, cet article propose de mettre en lumière les incohérences les plus manifestes entre fiction et réalité tout en rappelant que la voix n’est pas à proprement parler un indice biométrique qui peutêtre assimilé aux traces papillaires ou à l’ADN.
À travers le prisme pluridisciplinaire de la phonétique, du traitement du signal et des études visuelles, et sous l’œil des experts de la police scientifique, nous avons analysé plus d’une centaine de scènes de séries américaines impliquant une expertise du signal audio et, en particulier, de la voix. Nous tentons d’identifier des schémas récurrents qui contribuent à entretenir certains mythes liés à l’identification d’un individu par sa voix. Nous évaluons le degré de plausibilité de certains extraits et proposons les prémisses d’une esthétique de l’expertise vocale. Nous souhaitons ainsi mieux comprendre comment le grand public se représente les applications criminalistiques des sciences de la parole et espérons, en confrontant la fiction à la réalité, faire passer un message pédagogique à destination non seulement des téléspectateurs, mais également des professionnels de la police et de la justice.
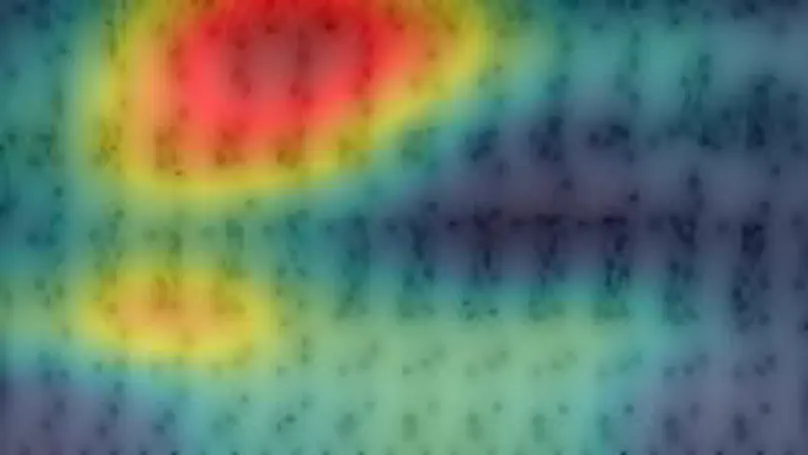
Des réseaux de neurones convolutifs ont été entraînés sur des spectrogrammes de voyelles /ɑ̃/ et de séquences aléatoires de 2 secondes extraites de 44 locuteurs du corpus NCCFr afin d’obtenir une classification de ces derniers. Ces deux modèles présentent une répartition équivalente des locuteurs dans l’espace acoustique, ce qui suggère que la classification a été faite sur des critères indépendants des phonèmes précis extraits. De multiples mesures phonétiques ont été effectuées afin de tester leur corrélation avec les représentations obtenues : la f0 apparait comme le paramètre le plus pertinent, suivie par plusieurs paramètres liés à la qualité de la voix. Des zones d’activation (Grad-CAM : Gradient-weighted Class Activation Mapping) ont été calculées a posteriori afin de montrer les zones spectrales et temporelles utilisées par le réseau. Une analyse quantitative de ces cartes d’activation a donné lieu à des représentations des locuteurs qui ne sont pas corrélées aux mesures phonétiques.

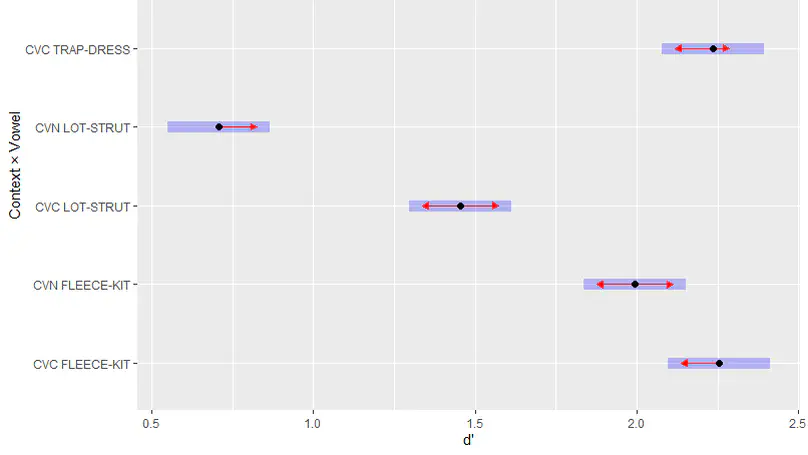
S’inscrivant dans la lignée de Trudgill (1983), cet article vise à comprendre le phénomène d’américanisation de la prononciation dans la voix chantée des artistes britanniques des années 1980. Le Heavy Metal a été sélectionné comme genre musical typiquement britannique à son origine, et étudié à l’aune de deux points de référence : la pop britannique et la pop américaine. Les voyelles de TRAP-BATH et LOT, dont les réalisations divergent entre les deux variétés d’anglais (britannique et américaine), ont fait l’objet d’analyses acoustiques chez six artistes. Nos résultats montrent qu’il existe un certain degré d’américanisation dans les productions chantées des artistes britanniques, qui est cependant plus marqué chez les groupes de Heavy Metal que chez les chanteurs de pop. La Discussion revient sur les divers types de paramètres (sociophonétiques, articulatoires, etc.) qui contraignent ce phénomène d’américanisation, et analyse la fiabilité des mesures acoustiques (formants et MFCC) calculées.
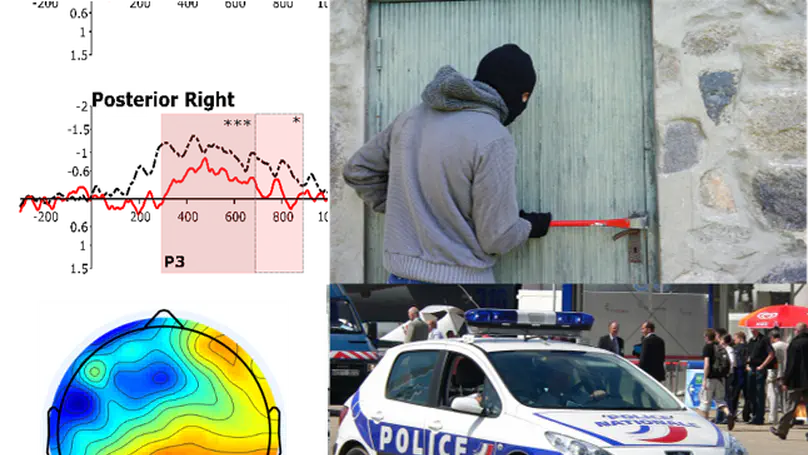
Our perception of someone’s accent influences our expectations about what they might say or do. In this experiment, EEG data were recorded while participants listened to cliché sentences matching or not the stereotypes associated with the speaker’s accent (upper-class Parisian accent or banlieue accent, a negatively connoted accent associated with youth from suburban areas; e.g. “I always listen to rap in my car” said with a banlieue accent (congruent) or an upper-class accent (incongruent)). Mismatches between social accent and stereotypical content triggered an event-related potential (ERP) known as the N400, albeit more anterior than the one observed for semantic violations, as well as a P3. These results are in line with other studies – conducted in particular with gender stereotypes – suggesting that stereotypes are stored in semantic categorical knowledge and that mismatches trigger integration difficulties and checking and updating mechanisms, and extend them to socially marked accents.
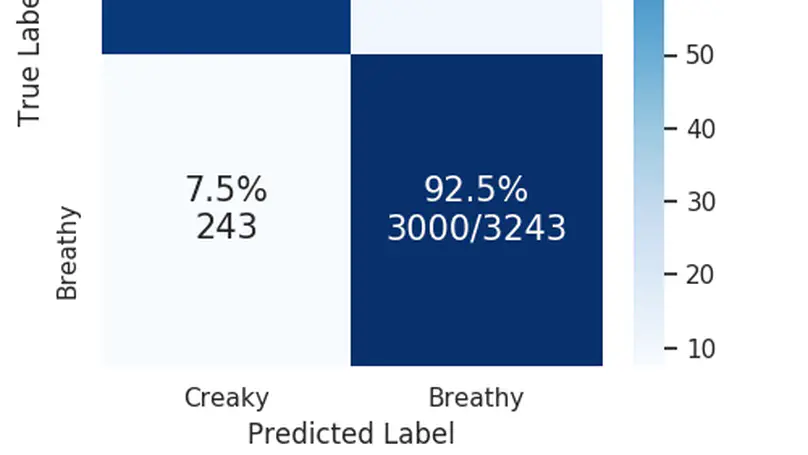
Voice quality is known to be an important factor for the characterization of a speaker’s voice, both in terms of physiological features (mainly laryngeal and suprala-ryngeal) and of the speaker’s habits (sociolinguistic factors). This paper is devoted to one of the main components of voice quality: phonation type. It proposes neural representations of speech followed by a cascade of two binary neural network-based classifiers, one dedicated to the detection of nonmodal vowels and one for the classification of nonmodal vowels into creaky and breathy types. This approach is evaluated on the spontaneous part of the PTSVOX database, following an expert manual labelling of the data by phonation type. The results of the proposed classifiers reach on average 85 % accuracy at the frame-level and up to 95 % accuracy at the segment-level. Further research is planned to generalize the classifiers on more contexts and speakers, and thus pave the way for a new workflow aimed at characterizing phonation types.
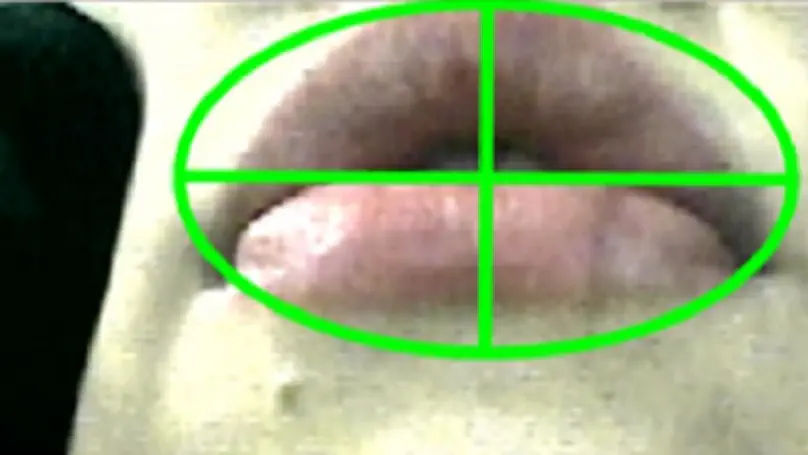
The secondary labial articulation which accompanies the post-alveolar approximant /r/ in English has attracted far less attention from linguists than the primary lingual one. However, the lips may be particularly important in the variety of English spoken in England, Anglo-English, because non-lingual labiodental articulations ([ʋ]) are on the rise. Labiodentalisation may be due to speakers retaining the labial gesture at the expense of the lingual one, implying that /r/ is always labiodental even in lingual productions. We verify this assumption by comparing the labial postures of /r/ and /w/ in Anglo-English speakers who still present a lingual component. If post-alveolar /r/ is labiodental, the labial gesture for /w/, which is unequivocally considered rounded, should differ considerably. Techniques from deep learning were used to automatically classify and measure the lip postures for /r/ and /w/ from static images of the lips in 23 speakers. Our results suggest that there is a recognisable difference between the lip postures for /r/ and /w/, which a convolutional neural network is able to detect with a very high degree of accuracy. Measurements of the lip area acquired using an artificial neural network suggest that /r/ indeed has a labiodental-like lip posture, thus providing a phonetic account for labiodentalisation. We finish with a discussion of the methodological implications of using deep learning for future analyses of phonetic data.
Second language (L2) learners frequently encounter persistent difficulty in perceiving certain non-native sound contrasts, i.e., a phenomenon called “phonological deafness”. However, if extensive L2 experience leads to neuroplastic changes in the phonological system, then the capacity to discriminate non-native phonemic contrasts should progressively improve. Such perceptual changes should be attested by modifications at the neurophysiological level. We designed an EEG experiment in which the listeners’ perceptual capacities to discriminate second language phonemic contrasts influence the processing of lexical-semantic violations. Semantic congruency of critical words in a sentence context was driven by a phonemic contrast that was unique to the L2, English (e.g.,/ɪ/-/i:/, ship – sheep). Twenty-eight young adult native speakers of French with intermediate proficiency in English listened to sentences that contained either a semantically congruent or incongruent critical word (e.g., The anchor of the ship/*sheep was let down) while EEG was recorded. Three ERP effects were found to relate to increasing L2 proficiency: (1) a left frontal auditory N100 effect, (2) a smaller fronto-central phonological mismatch negativity (PMN) effect and (3) a semantic N400 effect. No effect of proficiency was found on oscillatory markers. The current findings suggest that neuronal plasticity in the human brain allows for the late acquisition of even hard-wired linguistic features such as the discrimination of phonemic contrasts in a second language. This is the first time that behavioral and neurophysiological evidence for the critical role of neural plasticity underlying L2 phonological processing and its interdependence with semantic processing has been provided. Our data strongly support the idea that pieces of information from different levels of linguistic processing (e.g., phonological, semantic) strongly interact and influence each other during online language processing.
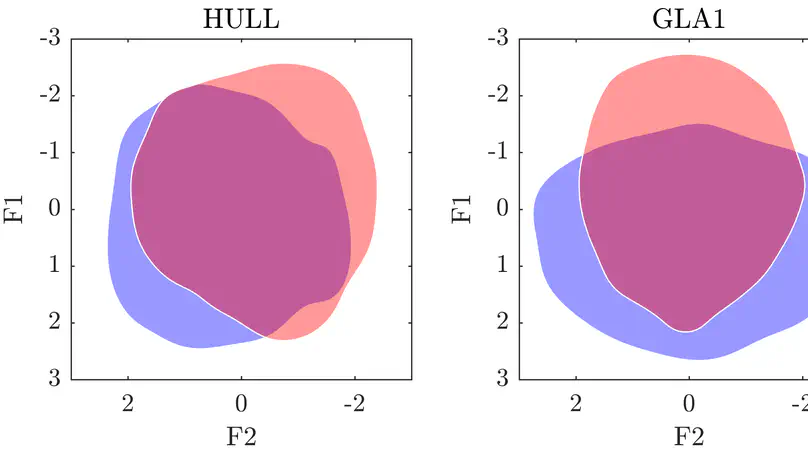
My goal is to examine acoustic and perceptual data from various locations in the British Isles – Enniskillen (Ulster), Glasgow, and Hull – in order to better understand the production and perception of certain Derived Phonological Contrasts found in English. This research falls within a broader framework that I call the Gradient Phonemicity Hypothesis (GPH), according to which a whole range of cognitive statuses is assumed to exist between allophony and phonemicity, and a difference between two sounds can be described by some measure of how typically allophonic or phonemic their relation is. In addition to the well-known attributes of maximal phonemicity – e.g. phonological unpredictability, high functional load/type frequency, etc. – it is my contention that a more thorough understanding of gradient phonemicity can be gained by analysing acoustic, articulatory and perceptual data.
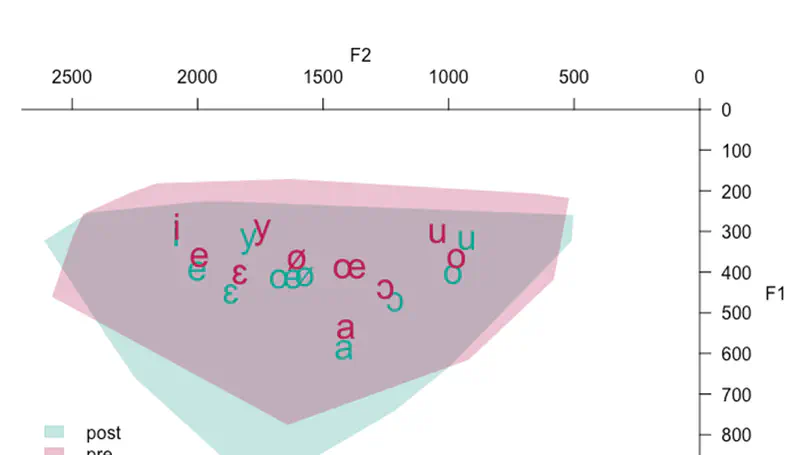
Objet : Notre recherche examine l’effet du Lee Silverman Voice Treatment (LSVT LOUD®) sur l’aire et la position de l’espace vocalique, la fréquence fondamentale (f0), les paramètres de qualité de voix, le débit de parole, le temps maximum phonatoire (TMP) et le ressenti de handicap vocal chez des patients francophones atteints de la maladie de Parkinson. Méthode : Un même protocole a été proposé en prétest et post-test à 12 patients parkinsoniens. Résultats : En post-test, nous observons une descente significative de l’espace vocalique, une différence de f0 entre la parole lue et la parole spontanée, une amélioration significative des paramètres de qualité de voix (jitter, shimmer, HNR) et du ressenti de handicap vocal. Le débit de parole des patients est maintenu, le TMP subit un effet de l’exercice.

Nous avons effectué une classification automatique de 44 locuteurs à partir de réseaux de neurones convolutifs (CNN) sur la base de spectrogrammes à bandes larges calculés sur des séquences de 2 secondes extraites d’un corpus de parole spontanée (NCCFr). Après obtention d’un taux de classification moyen de 93,7 %, les différentes classes phonémiques composant chaque séquence ont été masquées afin de tester leur impact sur le modèle. Les résultats montrent que les voyelles orales influent avant toute autre classe sur le taux de classification, suivies ensuite par les occlusives orales. Ces résultats sont expliqués principalement par la représentation temporelle prédominante des voyelles orales. Une variabilité inter-locuteurs se manifeste par l’existence de locuteurs attracteurs qui attirent un grand nombre de faux positifs et qui ne sont pas sensibles au masquage effectué. Nous mettons en avant dans la discussion des réalisations acoustiques qui pourraient expliquer les spécificités de ces locuteurs.
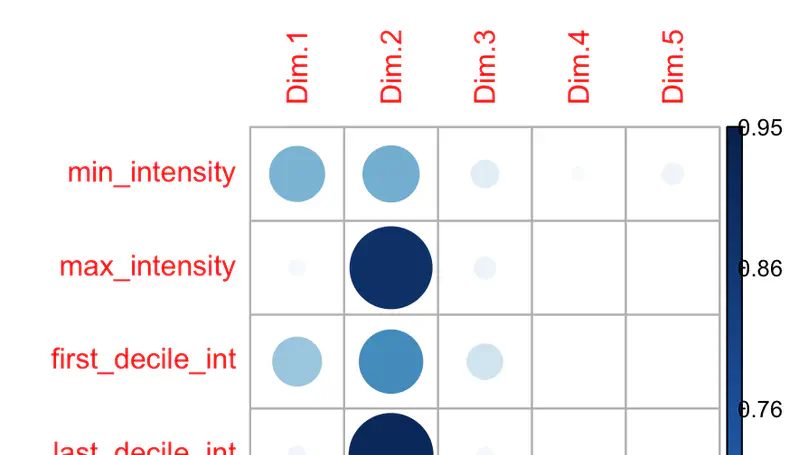
Dans ce travail nous avons recours aux variations de f0 et d’intensité de 44 locuteurs francophones à partir de séquences de 4 secondes de parole spontanée pour comprendre comment les paramètres prosodiques peuvent être utilisés pour caractériser des locuteurs. Une classification automatique est effectuée avec un réseau de neurones convolutifs, fournissant comme réponse des scores de probabilité pour chacun des 44 locuteurs modélisés. Une représentation par spectrogrammes a été utilisée comme référence pour le même système de classification. Nous avons pu mettre en avant la pertinence de l’intensité, et lorsque les deux paramètres prosodiques sont combinés pour représenter les locuteurs nous observons un score de classification qui atteint en moyenne 59 % de bonnes réponses.
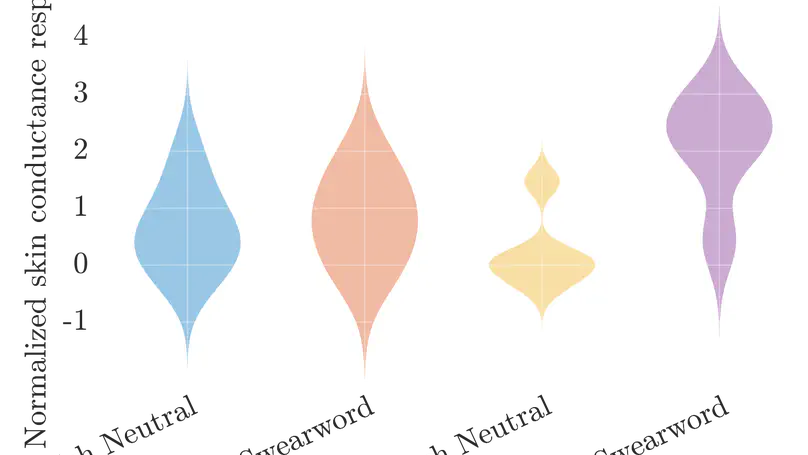
Hearing swear words or taboo words causes us discomfort. Research suggests that emotional responses caused by such words are stronger when the words are spoken in the listener’s first language (L1), rather than their second language (L2). We attempt to replicate these findings with a perceptual experiment. French learners of English were asked to listen to English and French swear words while their electrodermal activity (EDA) was monitored. Emotionally-neutral words were also included as baseline. EDA records small fluctuations in skin conductance caused by variations in the activity of sweat glands. Such variations are known to be correlated to the emotional state of the listener and reflect levels of stress or arousal in particular. We found a Word type ✕ Language interaction, which shows strong emotional reactions to swear words limited to the listener’s first language. This supports the claims that the L1 and L2 may be embodied differently, with the L2 being processed only semantically but not affectively. The role of different factors on L2 emotionality is discussed.
Articulatory variation of /r/ has been widely observed in rhotic varieties of English, particularly with regards to tongue body shapes, which range from retroflex to bunched. However, little is known about the production of /r/ in modern non-rhotic varieties, particularly in Anglo-English. Although it is generally agreed that /r/ may be accompanied by lip protrusion, it is unclear whether there is a relationship between tongue shape and the accompanying degree of protrusion. We present acoustic and articulatory data (via ultrasound tongue imaging and lip videos) from Anglo-English /r/ produced in both hyper- and non-hyperarticulated speech. Hyperarticulation was elicited by engaging speakers in error resolution with a simulated ``silent speech’’ recognition programme. Our analysis indicates that hyperarticulated /r/ induces more lip protrusion than non-hyperarticulated /r/. However, bunched /r/ variants present more protrusion than retroflex variants, regardless of hyperarticulation. Despite some methodological limitations, the use of Deep Neural Networks seems to confirm these results. An articulatory trading relation between tongue shape and accompanying lip protrusion is proposed.

OBJECTIVE: Interference suppression and response inhibition are distinct effortful inhibitory processes. Yet they rely on partly overlapping neural substrates. Their independence was studied using an auditory paradigm. METHOD: Continuous EEG was recorded in 16 adults and event-related potentials (ERPs) were analyzed in a new dichotic listening - Go/Nogo task. Attention was directed either to the right dominant ear (forced-right blocks [FR]) or to the left ear (forced-left blocks [FL]). The Go/Nogo task required a motor response only to the standard word played to the selected ear; the nonselected ear was simultaneously presented with the same word (Go condition) or with a deviant (Incongruent Go condition). In the Nogo condition, a deviant was presented to the selected ear while the standard was played to the nonselected ear. Effortful interference suppression was expected only in the FL blocks to override the automatic processing of distractors in the dominant ear. RESULTS: When no effortful interference suppression was necessary (FR blocks) in the Nogo condition, the N2 and P3 increase probably reflected two subcomponents of response inhibition (response restraint and response cancellation) and the P2 decrease probably reflected an early inhibitory mechanism (sensory gating). When effortful interference suppression was necessary (FL blocks), there was no Nogo-N2 (i.e., no response restraint). Interference suppression (Incongruent Go condition minus Go condition) also increased the N2 and P3, but did not modulate the P2. CONCLUSIONS: This new paradigm confirms the partial overlap between response inhibition and effortful interference suppression and points out specific features of their subcomponents.
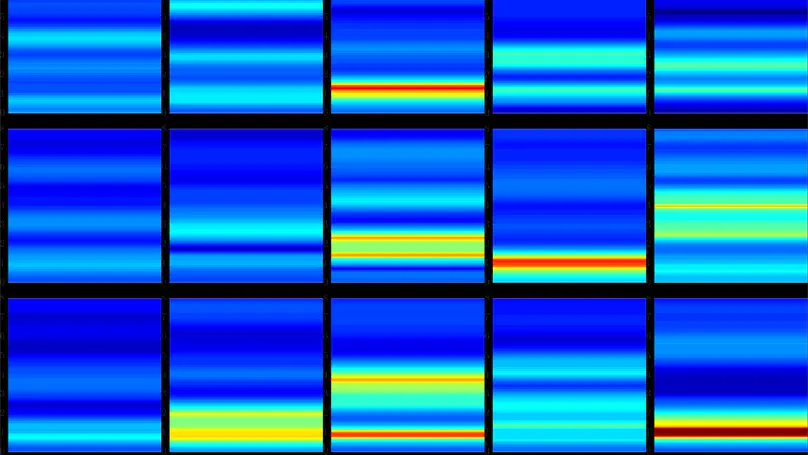
A deep convolutional neural network was trained to classify 45 speakers based on spectrograms of their productions of the French vowel /ɑ̃/ Although the model achieved fairly high accuracy – over 85 % – our primary focus here was phonetic interpretability rather than sheer performance. In order to better understand what kind of representations were learned by the model, i) several versions of the model were trained and tested with low-pass filtered spectrograms with a varying cut-off frequency and ii) classification was also performed with masked frequency bands. The resulting decline in accuracy was utilized to spot relevant frequencies for speaker classification and voice comparison, and to produce phonetically interpretable visualizations.
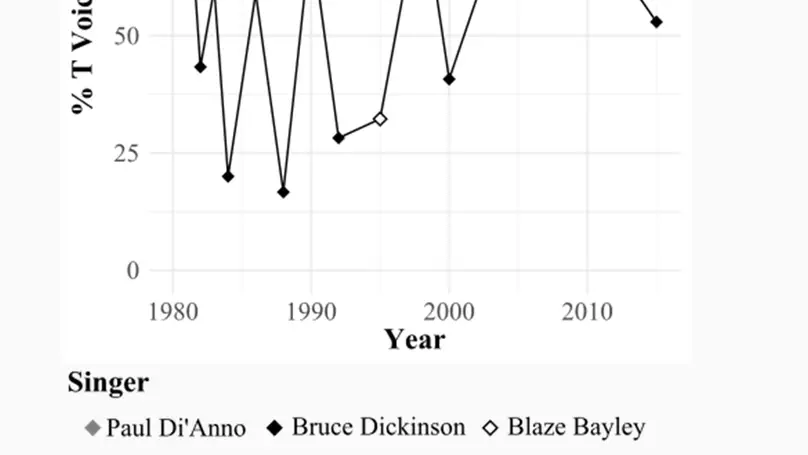
Drawing from Trudgill’s finding that some American phonetic features are common in British pop-songs, this paper explores whether this principle applies to a genre as distinctly British (in its original form) as Heavy Metal. We worked on a database comprised of the full studio discography, and some isolated vocal tracks and interviews of two bands: Iron Maiden and Def Leppard. We analyzed two phenomena: i) T Voicing as an index of Americanization and ii) if the typical Northern British lack of FOOT-STRUT Split found in Def Leppard’s interviews is preserved in songs. Results showed that a certain degree of Americanization is attested. While part of it can probably be attributed to Trudgill’s idea that the American cultural domination in the music industry leads to imitation, other factors come into play.

Broadband spectrograms of French vowels /ɑ̃/, /a/, /ɛ/, /e/, /i/, /ə/, and /ɔ/ extracted from radio broadcast corpora were used to recognize 45 speakers with a deep convolutional neural network (CNN). The same network was also trained with 62 phonetic parameters to i) see if the resulting confusions were identical to those made by the CNN trained with spectrograms, and ii) understand which acoustic parameters were used by the network. The two networks had identical discrimination results 68% of the time. In 22% of the data, the network trained with spectrograms achieved successful discrimination while the network trained with phonetic parameters failed, and the reverse was found in 10% of the data. We display the relevant phonetic parameters with raw values and values relative to the speakers’ means and show cases favouring bad discrimination results. When the network trained with spectrograms failed to discriminate between some tokens, parameters related to f0 proved significant.

Few studies have investigated the influence of body posture on speech production and especially on its acoustic parameters. This study examines the influence of supine and upright position on the formants (F1 and F2), of the 10 French oral vowels, on F0, on speech rate and on the characteristics of the electroglottographic signal. The small differences observed between the two conditions highlight the speakers’ ability to compensate for the effects of gravity in an attempt to preserve the acoustic characteristics of speech.

This paper studies the use of a lip retractor as a potential technique for phonetic studies involving perturbation. This device is currently used by participants of the internet sensation, the so-called ‘’no lips’’ or ‘‘mouth guard’’ challenge. Wearing the device restricts the use of the lips during speech. We present acoustic and articulatory data from four speakers of British English. Accelerometer data is used to assess the dynamics of the jaw and ultrasound tongue imaging gives us insights into potential compensation strategies, specifically for the /u/ (GOOSE) vowel. Ultrasound data revealed that three speakers showed signs of tongue retraction for perturbed /u/, which was not reflected in the corresponding acoustic data. This study highlights the limitations of a purely acoustic analysis of the effects of perturbation on speech. Despite certain limitations, we conclude that the use of the lip retractor is a promising technique for future lip perturbation studies.

Like every late L2 - learner, French native speakers are characterized by a foreign accent. The literature emphasizes that the vowels / ɪ /, / ʌ / and / æ / in particular are pronounced ‘‘à la française’’. This study presents the acoustic parameters of the English vowels / ɪ /, /i:/, / æ /, / ʌ / and / ɑ: / produced by 38 native English speakers and 48 French learners of English compared to those of the French vowels / a /, / e /, / i / et / œ / produced by the same learners. The results first show more variability in the L2 compared to L1 productions. Furthermore, we observe a great confusion between categories in L2 for the /i: - ɪ / contrast and the opposite effect in the region of the [a]. We show that L2 learners did produce duration contrasts but not to the same extent as the natives . Finally, the formant dynamic analysis of / i: / and / i / may suggest that the English native speakers do not all produce a diphthongal / i: /.
